We were talking not long ago about universal basic income policy, and there were a variety of opinions about the desirability, political sustainability and implications of such a policy. But, before arguing about those issues, it’s useful to consider whether a basic income is feasible at all and, if so, what kinds of tax policies, and adjustments to other welfare policies, would be required to support it. I’ve considered the relatively easy case of a guaranteed minimum income, rather than a universal basic income paid to everyone, as advocated by Philippe von Parijs and others.
Justin Fox has a “piece”:http://blogs.hbr.org/fox/2012/08/the-wall-street-book-everyone.html on Doug Henwood’s wonderful book, _Wall Street_
bq. These days, it’s not hard to find people who question the role that financial markets play in our economy, who argue that shareholder value is a flawed metric of corporate success, who say that linking pay to financial markets is a big mistake. In 1997, though, such arguments were pretty close to unheard of. Which is what makes Doug Henwood’s book _Wall Street,_ published that year, such an amazing document. Along with explaining in clear if caustic terms how financial markets work, the book prefigures almost every criticism of the financial system that’s been levied since the crisis of 2008. An overleveraged housing market? Check. A link between financial sector growth and income inequality? Check. A natural tendency toward instability in financial markets? Check. … There’s a saying in investing that “being early is the same as being wrong.” It’s not _quite_ like that in intellectual endeavors, but Henwood clearly hasn’t gotten his due. That’s partly because he was early, partly because he operates in an ill-defined border zone between journalism and academia, partly because, well, he’s a crotchety leftist. But he was describing a lot of important problems with the workings of our capitalist system at a time when practically everyone else was proclaiming the brilliance of the shareholder-dominated Wall Street way. We should have been listening to him then, and we should be rereading him (or reading him for the first time) now.
The “book is available for free download here”:http://wallstreetthebook.com/ (with a suggested donation to the author, who got a relative pittance for writing it; left-leaning publishers sometimes treat their authors like shit). It’s every bit as good as Fox says it is and better – there’s a very strong argument that it’s the best leftwing book on actually-existing-capitalism that’s been written in the last couple of decades. It _is_ a little out of date – a lot has changed in the intervening years. I would love to see an extensively updated second edition, both for purely selfish reasons, and because I think that it could play an important intellectual and political role (most people on the left don’t understand how finance markets actually work). From various conversations, I’m sure that I’m not the only person who thinks this. The obvious way to get such an edition going – if Doug were interested in writing it – would be a Kickstarter or similar. But it might help encourage Doug to do this if there were some evidence of public interest beforehand (again: if he wants to do this – I have not consulted him before writing this). Hence this post – if you would be prepared to kick in to see this book written then say so in comments, or elsewhere as you like. I’m in for a commitment of $100 or over myself (nb that this is _not_ a suggested donation – more a credible commitment and a signal that I personally really, really would love to see this book come into being).
{ 111 comments }
Hi there liberal rule-of-law fetishists!
Now that I’ve got your attention, I’d like to mention something that’s been bothering me. This idea that we all order our affairs under a system of predictable rules sounds very nice, but I do wonder whether it’s compatible with some of the other things that you seem to be signed up for. Some of you, I know, are worried about this so-called 1 per cent, and even about the 1 per cent of the 1 per cent: the people who own lots of stuff. Not only do they own lots of stuff, but they own the kind of stuff that is useful if you want to own even more stuff. That’s how it goes. And, of course, they also have the means to bring about a favourable “regulatory environment”, so that they get to hold onto that stuff.
Now I suppose you want to do something about that? Yes? One option would be to let them hang onto all their existing assets – after all, they got them justly (or at least non-criminally) according to the rules of the system they themselves helped to formulate – but to introduce a new system of rules (call it a “basic structure” if you like) that works to the greatest benefit of the least advantaged. Assume you have the knowledge to design it with the distributive effects you want (big assumption that!). Let that system grind away for long enough – a few generations perhaps – and you’ll have shifted things a little bit in the right direction. (Assuming, that is, that the 1 per cent don’t use their residual wealth and influence to throw you off-track as soon as you hit the first bump.)
I think you can see where I’m going by now. If you really want a shift in the distribution of wealth and income, if you really really want it, then realistically you’re going to have to use state power to do a bit of _ex post_ redistribution. You’re going to have to take stuff from some people and give it to others. Doesn’t necessarily have to be that total Marxian expropriation of the expropriators: a comprehensive programme of debt cancellation would fit the bill. Life is about making choices: and you’re going to have to choose. Is it outrageous to dispossess someone of the wealth they acquired under the rules of the game; or are you going to say that substantive fairness sometimes matters more?
Now I know there are some wrinkles there. What about predictability? What about incentives? Sure. (Of course the predictability of stable property rules is a bit overstated: all those people who got their houses repossessed when the economy went bad didn’t see that coming!) You might have to duck and weave. You might have to convince property owners that you’ll only go so far and no further. But don’t kid yourselves that you can do the redistribution you want and treat the rule of law as absolute. If robbing the rich appals you, become a libertarian instead.
(UPDATE: Well I’ve clearly managed to confuse a bunch of people with this post. Probably a consequence of trying to make a serious point in a knockabout style. I had in mind not any old garden-variety idea of the rule of law but something a bit more specific, namely that society ought to be run according to predictable rules that provide individuals with certainty that their efforts won’t be nullified by state action, a view associated with Hayek but endorsed by Rawlsians. So _mea culpa_ for that.)
{ 220 comments }
Discussion of those badminton players seems to divide into two camps: those who think it is fine to exploit the letter of the law to gain strategic advantage and therefore can’t see a problem, and those who don’t. Bracketing off for a second the embarrassing fact for those in the first camp that there does actually seem to have been a rule against deliberately losing, it’s plain that this is just a particular instance of a more general syndrome. There are people who devise and employ elaborate schemes to evade or avoid (I never know which is which) their taxes whilst staying just within the law. There are bankers who stay technically within a literal interpretation of the banking regulations, whilst engaging in dubious practices which undermine the regulator’s intention. There are employers who try to evade workplace regulations by reclassifying their workers as independent contractors. There are states which harp on about the technical details of the laws of war as they happily murder civilians. Well sometimes we need to punish the technically innocent but morally culpable. And it helps _encourager les autres_ to internalize the ethos behind the laws rather than seeing them as being just an inconvenient system of traffic control.
Rule-of-law fetishists, Hayekians, and the like tend to think this is just appalling. Legislators, regulators, sports administrators and similar, should devise watertight systems of rules within which people are entitled simply to go for it. But it is highly questionable that such watertight frameworks are possible, even in principle. So we need to give the enforcers some discretionary power to zap the bad people: people who knew perfectly well that what they were doing was at or over the moral and legal boundaries but didn’t care. (On the tax front, the UK’s plan to introduce a General Anti-Avoidance Rule is designed to punish just these characters.) Such power is, of course, liable to abuse. But that’s just the way things unavoidably are. The solution is not to pretend that we can make the rules work perfectly, but to make sure the enforcers are genuinely democratically accountable and removable.
{ 113 comments }
A family friend, Susi, just turned 90. Since I’m home in Oregon, I attended the B-Day party. Her Jewish family got out of Germany in ’39 and she found herself a teenager in the US. Got an education, got married, raised a family. She was – is – an artist, and she ended up teaching. But she worked as a gag strip cartoonist in New York, from ’46 to ’50. I’m interested in the history of comics, so she loaned me a rather large file box (which I am being very careful with!) Lots of old clippings, old battered bristol board with typed captions taped on. Neat! [click to continue…]
{ 28 comments }
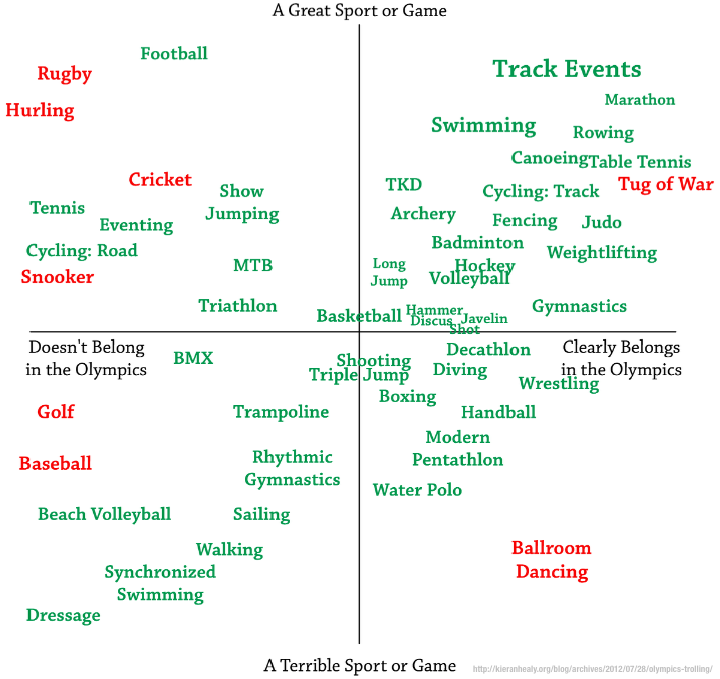
It’s that happy time when I whine about American television coverage of the Olympics. This year’s whining has a new twist—beyond the usual complaints about sentimental crap and tape-delay—given the lack of decent streaming options absent a pre-existing subscription to some cable channels. But it’s also the time when I’m reminded of my existing personal prejudices about sports, when I may discover new ones (as new events are added), and when I try to figure out whether there’s any defensible rationale to my preferences. Reflecting on my sports bigotry, I think the simplest model is a two-dimensional space that, I think you will agree, is both easy to understand and wholly objective.
{ 220 comments }
While working on a piece about a possible bailout for the Spanish government, I discovered a couple of things that were news to me
* The Economics Minister in the (pro-austerity) Spanish government is a former executive of Lehman Brothers
* Axel Weber, formerly the ultra-hawkish head of the Bundesbank went straight from that job to the chairmanship of UBS, of which the NYT recently wrote “The bank’s recidivism seems rivaled only by its ability to escape prosecution”
Comment seems superfluous to me, but I hope readers will prove me wrong on this.
{ 20 comments }
Following up Henry’s post, my Dark Knight Rises take is this. The Nolan brothers are determined to make some kind of serious, dark, brooding, non-fascistic moral sense of Batman, and that’s just flat-out impossible. Can’t tell it that way without the basic story logic boxing you into a place you don’t want to be (as Henry says, there’s too much baked in the cake). If what the world needs is masked vigilantes behaving in this crazy way, then fascism needs a serious look-in as a political philosophy. But what we should really conclude is not that the moral sense of the film is fascist – or even aristocratic. Rather, we should conclude that the film makes no moral sense whatsoever. It conveys no moral message. It’s morally illegible. Lots of explosions and fighting. That’s it. [click to continue…]
{ 88 comments }
A short note on something I’d like to have time to write about at further length someday. There’s a common perception among US lefties that Northern European states like Germany are (or at least were, until recently) the land of milk, honey, and organized capitalism. But actual European social democrats have more complicated feelings about organized capitalism than most of their American counterparts. “Helen Callaghan and Martin Höpner”:http://www.mpifg.de/people/hc/Publications/documents/2011-12-16%20Changing%20Ideas%20resubmitted%20to%20WEP.pdf have an interesting recent paper on this topic. As they point out, German social democrats used once upon a time to be in favor of organized capitalism, comfortable monopolies and so on. But then – Hitler!
bq. Organized capitalism appears conducive to leftist aims as long as the focus is on its contribution to economic coordination, and this explains the supportive attitudes of the German left up to the early 1930s. However, besides economic coordination, organized capitalism also affects political organization, as German labor leaders learnt painfully during the Nazi period. The radical reversal of attitudes after World War 2 reflects updated beliefs regarding the political consequences of organized capitalism, and the greater weight assigned to political over economic considerations. … Far from being a fleeting phenomenon, Leftist support for competition policy and market-enhancing corporate governance reforms has characterized German party politics throughout the post-war period. … During the “seven-year cartel battle” that led to the toothless competition law of 1957, the SPD supported the liberal ideas of chancellor Ludwig Erhard (CDU), unlike the majority of CDU/CSU representatives. … The joint-stock law reform of 1965, which ended up smaller than intended, featured a similar constellation. … Passage of a company network dissolution act that would have limited bank shareholdering in industrial companies was only prevented by the SPD’s removal from office in 1982. In 1998, during debates over the Control and Transparency Act introduced by Helmut Kohl’s CDU/CSU/FDP coalition, Social Democrats emerged as more favorable to radical corporate governance reforms than the Christian Democrats …. In 2001, during negotiations on the Takeover Act, the SPD turned down CDU demands to strengthen managerial defenses against hostile takeovers.
The logic here is pretty straightforward. Social democrats would like an organized economy in the best of all possible worlds. However, the more organized the economy is in actually existing capitalism, the more _political power_ accrues to big industrialists, and the more likely it is that they will use that power in the political realm in ways that disadvantage labour. Hence, the question of whether or not to favor an organized economy is an empirical one, and under many circumstances, leftists can be vehemently, and entirely consistently, in favor of market competition (albeit for political as well as/instead of economic efficiency reasons).
While I don’t have time to write much on this today, it’s relevant in the US as well as the EU context. “Karl Bode”:http://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2012/07/op-ed-verizon-willfully-driving-dsl-users-into-the-arms-of-cable/ has an interesting piece in _Ars Technica_ on Verizon’s cable strategy.
bq. Back in April, you may recall that Verizon stopped selling standalone DSL, taking us back to the stone age of broadband when users were forced to bundle a costly landline they might no longer want. … Verizon has numerous reasons for wanting its DSL services to die off, including the fact that newer LTE technology is cheaper to deploy in rural areas and easier to keep upgraded. But one of the driving forces is that Verizon is eager to eliminate unions from the equation, given that Verizon Wireless is non-union. None of this is theory; in fact, it has been made very clear by Verizon executives. … It’s all an ingenious play by Verizon, though it will have a massive competitive and connectivity impact on the US broadband market that will be studied for decades. What’s most amazing is that nobody (analysts, regulators, or the press) seems to have really noticed what Verizon is up to: turning a massive swath of the country from a marginally competitive duopoly with union labor into an even less competitive and more expensive cable and telco non-unionized cooperative monopoly.
I’m not an expert on telcos, so can’t speak to the accuracy of this analysis. But if it’s right, it suggests a roughly similar logic. Labour unions prefer, _ceteris paribus_, to deal with large well-established incumbents than a congeries of smaller firms. The organizing costs are lower, and incumbents are more likely to have profits that they are prepared to share in order to guarantee predictability. However, once firms start getting _too_ big, they may be too powerful, in terms both of political and economic clout, for unions to bring to the negotiating table. They can furthermore redefine the market (as Verizon is plausibly doing) in ways that weaken unions and make it harder to organize. This makes me think that there’s more scope for a genuinely left-wing anti-monopoly movement (especially in sectors such as telecommunications, which are vulnerable to regulatory capture) than common perceptions would suggest. I’d really want to re-read JK Galbraith’s work to think this through properly. But since I’m crashing on a couple of deadlines, I’ll leave it for commenters to thresh out …
{ 68 comments }
Attention conservation notice: contains spoilers and copious idle speculation about the Deep Political Meaning of popular cultural artifacts of the kind that is barely tolerable at blogpost-length, and surely intolerable beyond it.
I saw _Batman: The Dark Knight Rises_ on Saturday (I was a little nervous about copycat shootings). It has some excellent set-pieces, but is not a great movie. If the standard is ‘better than _The Godfather Part III_,’ it passes muster, but by a rather narrower margin than one would like. It wants to be an _oeuvre_, saying serious things about politics and inequality, but doesn’t ever really get there. This “Jacobin piece”:http://jacobinmag.com/blog/2012/07/the-dark-knight-is-no-capitalist/ by Gavin Mueller argues that it’s not a pro-capitalist movie, but a pro-monarchist one. I think that’s wrong. It’s a _pro-aristocratic_ movie, which isn’t really the same thing. Mueller’s observation that:
bq. There is barely any evidence of “the people” at all – it’s all cops and mercenaries battling it out. So instead of a real insurrection, the takeover of Gotham functions via Baroque conspiracies among elites struggling for status and power.
is exactly right – but a movie about “elites struggling for status and power” without some master-figure, however capricious, who can grant or deny them recognition isn’t actually about monarchy. It’s about the struggle between the elites themselves.
{ 69 comments }
After nearly 10 years, military trials at the Guantanamo Bay Detention Camp have produced a total of six convictions. One of those was Australian David Hicks, who agreed to a plea bargain under which he would be sent back to Australia to serve out his sentence. On his release, he wrote a book about his experiences. Under Australian “proceeds of crime” laws, the earnings from books about a criminal career are liable to confiscation, and the Australian government accordingly froze the proceeds and took action to have them forfeited.
The news today is that the Director of Public Prosecutions has abandoned the actions and paid Hicks’ legal costs[1]. Although no rationale was given, the general presumption is that the US conviction would not stand up in an Australian court, either because (as Hicks alleged) Hicks’ guilty plea was extracted by torture, or because the whole system failed to meet basic standards of due process. Most simple of all is the fact that, unlike the usual case of plea bargaining, the options aren’t pleading guilty or going to trial. Rather those who plead guilty get a definite (and usually relatively short) sentence on top of their detention, while those who do not are held indefinitely without trial.
All of this is relevant now that the Obama Administration is trying to “normalise” the plea bargaining process, by getting those who have pleaded guilty to testify against others accused of more serious crimes. The idea that the state can torture someone, imprison them indefinitely, and then use their “voluntary” testimony (given in the hope of release) against another, then claim that this is an improvement on using confessions extracted by torture of the accused is more reminiscent of the legalisms of a totalitarian state than of anything that could be described as the rule of law.
fn1. The only other Australian detainee, Mamdouh Habib, was threatened with similar action, but this did not proceed. He eventually received a substantial (but secret) settlement in return for dropping claims against the Australian government for its alleged involvement in his torture.
{ 10 comments }
Some time in 2009, I was sitting on a bar stool in Dulles Airport, killing an hour or two before a delayed flight back to the west coast. It was one of those horse shoe bars, and I was the only woman. The half a dozen or so suited men were being conspicuously polite about not imposing themselves, but I was feeling quite open to some company for the wait. I raised my glass to the two nearest guys and we got chatting. I was on white wine, and they were on whiskey. After a drink, one of them left to get his flight. The remaining guy stuck around. He was an ex-marine and very good company. He was itching to tell a story, but also kind of averse, so I sat back and let him come to it in his own time.
His old job at the Pentagon had been to sit in a single office and man two phones. One phone was for receiving calls through the public phone system. The other one, he simply picked up and it automatically went through to a blocked internal number. Every so often, the receiving call would ring. It would be a member of the public who wanted to report extra-terrestrial activity; strange lights, crop circles, abductions, whatever. Usually, though, just the strange lights. The guy would write down all the details verbatim, thank the caller for their information, and hang up. Then, he’d pick up the other phone, pass the details along to an unnamed individual, and hang up. And that was it. For two years, he recorded alien-sightings from the public and passed them to someone or other in the military chain of command.
The story tickled me. Not least, because it’s so inconclusive. You can see why the US military would want to keep tabs on sightings of odd-looking aircraft. (I still remember seeing the Stealth bomber parked in Dublin airport a while back and finding it hard to believe it was human tech.) But also, it’s kind of delicious to think the Pentagon is paying a little attention to stuff randomers see and report, just in case it turns out to be aliens.
Of course, the US is not the only country in the world trying, discreetly, to keep an open mind on intelligent, extra-terrestrial life. Recently, the UK’s National Archive opened some files about UFO sightings in Britain. The BBC news story says that between “1950 and 2009, a special Ministry of Defence unit investigated more than 10,000 UFO “sightings” – a rate of one every two days.” The unit followed the same model as my bar-buddy’s; a public hotline and a single staffer whose job was to record and refer. The more you look at the types of things recorded, the more it seems that it’s simply a way to keep track of all-too-terrestrial unexplained happenings in the sky.
All the same, I’m with Stephen Hawking on this; if more intelligent and inter-galactically mobile life exists out there, I very much hope they neither discover nor take any notice of us.
{ 72 comments }
The chart in “America is a Violent Country” has been getting a lot of circulation. Time to follow up with some more data. As several commentators at CT noted, the death rate from assault in the U.S. is not uniform within the country. Unfortunately, state-level and county-level mortality data are not easily available for the time period covered by the previous post—though they do exist, going back to the 1940s. What I have to hand is a decade’s worth of US mortality data courtesy of CDC WONDER covering 1999 to 2009. I extracted the assault deaths according to the same criteria the OECD uses (for the time period in question, ICD-10 codes X85-Y09 and Y87.1). The estimates are adjusted to the 2000 U.S. population, which isn’t identical to the standard OECD adjustment. But the basic comparability should be OK, for our purposes.
First, it’s well-known that there are strong regional differences in the assault death rate in the U.S. by state and region. Here’s what the patterns look like by state from 1999 to 2009.
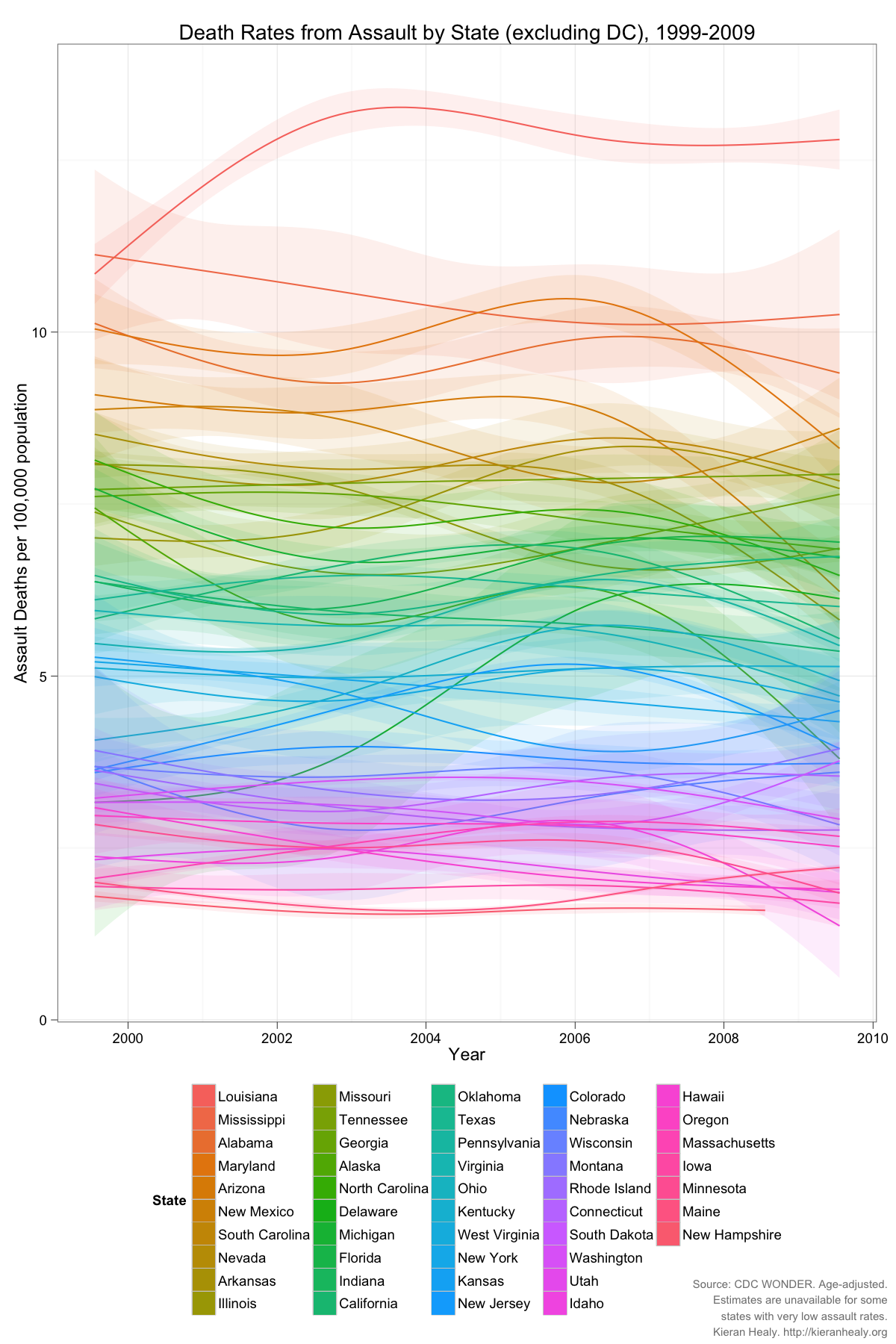
Trends in the Death Rate from Assault, 1999–2009, by State. Click for a larger PNG or PDF.
[click to continue…]
{ 90 comments }
I’m on holiday, so here’s some. ‘Language’ in the sense of ‘YouTube video of old Beyond The Fringe sketch’, that is. “There’s too much Tuesday in my beetroot salad.” How has this failed to become a classic example, or at least a ‘classic example’? Why do people think it’s appropriate to go on chomping on Chomsky’s colorless greens when you have an alternative like that? Back to the roughage grounds! “I don’t think you’re saying, I don’t think you’re saying – I don’t say you’re thinking.” Now just ‘go on in the same way,’ as they say.
Link.
Is Alan Bennett supposed to be Austin? Whose mannerisms are being spoofed?
{ 23 comments }
The terrible events in Colorado this morning prompted me to update an old post about comparative death rates from assault across different societies. The following figures are from the OECD for deaths due to assault per 100,000 population from 1960 to the present. As before, the most striking features of the data are (1) how much more violent the U.S. is than other OECD countries (except possibly Estonia and Mexico, not shown here), and (2) the degree of change—and recently, decline—there has been in the U.S. time series considered by itself. Note that “assault” as a cause of death does not distinguish the mechanism of death (gunshot, stabbing, etc). If anyone knows of a similar time series for homicides specifically, let me know.
Here are the individual time series.
{ 154 comments }